GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)
GERD is a chronic disease that happens when stomach acid flows into the esophagus and causes irritation. Two main types of GERD are Non-Erosive GERD and Erosive Esophagitis (EE).
Who does GERD affect?
GERD is one of the most common digestive diseases, affecting approximately 65 million people in the United States.

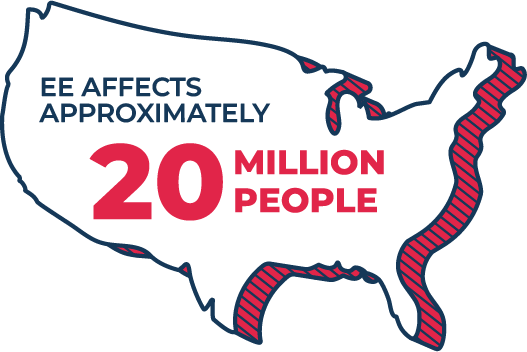
EROSIVE ESOPHAGITIS (EE) VS NON-EROSIVE GERD

EE is a type of GERD in which acid-related damage to the esophagus occurs. Non-Erosive GERD does not involve damage to the esophagus and is more common. Heartburn is common in both conditions.

HEARTBURN THAT PERSISTS

Many people with EE continue to feel acid in their esophagus despite taking medicines such as antacids, histamine-2 receptor antagonists (H2s), or proton pump inhibitors (PPIs).

AVAILABLE TREATMENTS FOR GERD
Not all treatments work for everyone. It’s important to talk to your doctor about treatments that are right for you. If you think you might have GERD, know that you’re not alone.

The first antacid was approved for use
Antacids neutralize the acid in your stomach to help relieve heartburn. They are typically offered over the counter and are used for symptom relief.

The first histamine-2 receptor antagonist (H2) was approved for use
H2s reduce the amount of acid produced in the stomach by blocking one of the first steps in acid production. H2s treat heartburn symptoms related to GERD.

The first proton pump inhibitor (PPI) was approved for use
PPIs are a common treatment for GERD. They treat GERD by blocking the final step of acid production. They are activated by stomach acid and most PPIs must be taken 30-60 minutes prior to meals.
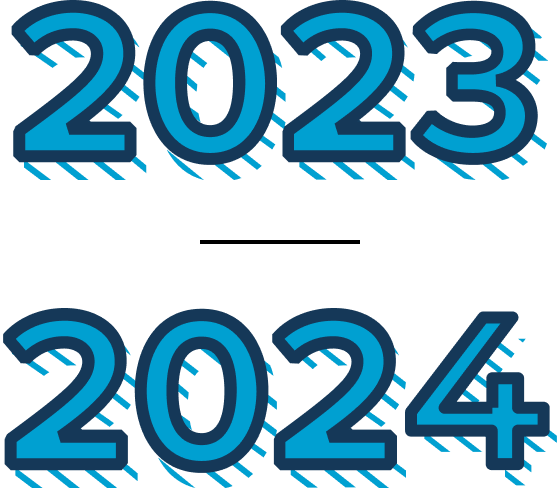
VOQUEZNA (vonoprazan) was approved for use as the first potassium-competitive acid blocker
VOQUEZNA was approved as the first potassium-competitive acid blocker (PCAB) to treat EE and its symptoms in 2023 and later to relieve heartburn caused by Non-Erosive GERD in 2024. PCABs work by blocking the final step of acid production—they do not need to be activated by stomach acid and can be taken with or without food.
FACTORS THAT MAY INCREASE YOUR CHANCES OF DEVELOPING GERD INCLUDE:
- Hiatal hernia
- Obesity
- Lower esophageal sphincter doesn‘t close correctly
- Delayed stomach emptying
SYMPTOMS RELATED TO GERD
The most common symptoms are heartburn and acid regurgitation. Other possible symptoms include:
- Difficult or painful swallowing
- Chronic cough
- Chest pain
HOW IS GERD DIAGNOSED?
To diagnose GERD, your doctor will ask you a few questions, and may perform a physical exam. To diagnose EE, an endoscopy is needed. An endoscopy is a procedure in which a thin tube equipped with a tiny camera is lowered down your throat.
STILL DEALING WITH PAINFUL HEARTBURN SYMPTOMS?
It may be time for a different approach. Connect with a telehealth provider to see if VOQUEZNA could be your next step to seek relief.
Phathom is providing this link to a third-party website to help patients connect virtually with an independent healthcare provider. Phathom does not own or operate the third-party site and does not endorse or recommend any of the healthcare providers associated with the third-party site. You are responsible for assessing the qualifications of the healthcare provider and any medical advice that is provided.
